专栏目录
- 1-Spring架构源码分析-Spring源码搭建
- 2-Spring架构源码分析-SSM框架说明
- 3-Spring架构源码分析-spring体系
- 4-Spring架构源码分析-Spring IOC机制设计思想和源码解读
- 5-Spring架构源码分析-Spring IOC之 Spring 统一资源加载策略
- 6-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之加载 BeanDefinition
- 7-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之注册 BeanDefinitions
- 8-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之解析Bean:解析 import 标签
- 9-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之解析 bean 标签:开启解析进程
- 10-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之解析 bean标签:BeanDefinition
- 11-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之注册解析的 BeanDefinitions
- 12-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之装载 BeanDefinitions 总结
- 13-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之开启 Bean 的加载
- 14-Spring架构源码分析-IoC 之加载 Bean:总结
- 15-Spring架构源码分析-Spring代理与AOP
- 16-Spring AOP源码分析-@EnableAspectJAutoProxy和AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
- 17-Spring AOP源码分析-AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
- 18-Spring AOP源码分析-AOP与BeanPostProcessor处理器
- 19-Spring AOP源码分析-代理对象调用目标方法
- 20-spring mvc设计思想和源码解读-spring mvc 功能特性
- 21-mvc 体系结构源码详解
- 22-Spring MVC源码跟踪
- 23-Spring事务源码分析
Spring MVC源码跟踪
mvc 各组件执行流程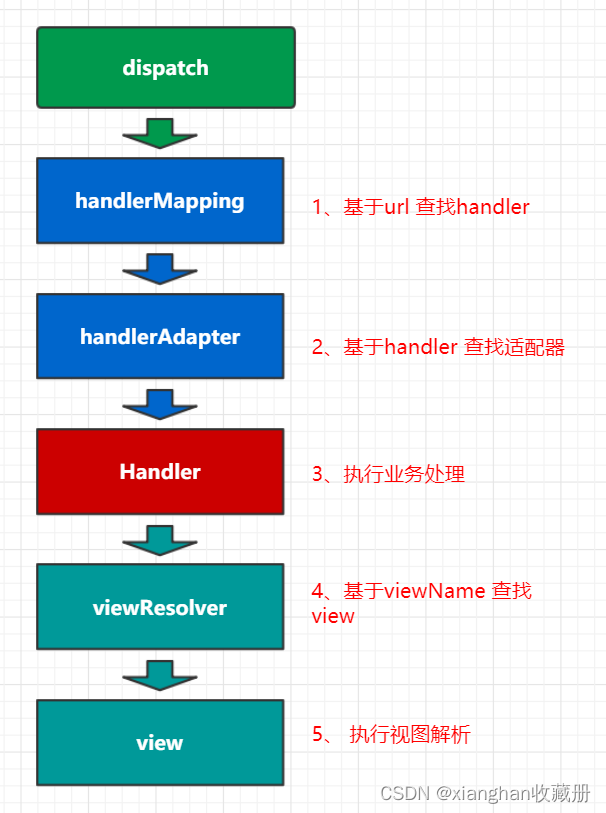
1.建立Map<urls,controller>的关系
我们首先看第一个步骤,也就是建立Map<url,controller>关系的部分。第一部分的入口类为ApplicationObjectSupport的setApplicationContext方法。setApplicationContext方法中核心部分就是初始化容器initApplicationContext(context),子类AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping实现了该方法,所以我们直接看子类中的初始化容器方法。
public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException {
super.initApplicationContext();
detectHandlers();
}
/**
* 建立当前ApplicationContext中的所有controller和url的对应关系
*/
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
// 获取ApplicationContext容器中所有bean的Name
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// 遍历beanNames,并找到这些bean对应的url
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 找bean上的所有url(controller上的url+方法上的url),该方法由对应的子类实现
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
// 保存urls和beanName的对应关系,put it to Map<urls,beanName>,该方法在父类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中实现
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified");
}
}
}
}
/** 获取controller中所有方法的url,由子类实现,典型的模板模式 **/
protected abstract String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName);
determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName)方法的作用是获取每个controller中的url,不同的子类有不同的实现,这是一个典型的模板设计模式。因为开发中我们用的最多的就是用注解来配置controller中的url,DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping是AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping的子类,处理注解形式的url映射。所以我们这里以DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping来进行分析。我们看DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping是如何查beanName上所有映射的url。
/**
* 获取controller中所有的url
*/
protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
// 获取ApplicationContext容器
ApplicationContext context = getApplicationContext();
//从容器中获取controller
Class<?> handlerType = context.getType(beanName);
// 获取controller上的@RequestMapping注解
RequestMapping mapping = context.findAnnotationOnBean(beanName, RequestMapping.class);
if (mapping != null) { // controller上有注解
this.cachedMappings.put(handlerType, mapping);
// 返回结果集
Set<String> urls = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// controller的映射url
String[] typeLevelPatterns = mapping.value();
if (typeLevelPatterns.length > 0) { // url>0
// 获取controller中所有方法及方法的映射url
String[] methodLevelPatterns = determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, true);
for (String typeLevelPattern : typeLevelPatterns) {
if (!typeLevelPattern.startsWith("/")) {
typeLevelPattern = "/" + typeLevelPattern;
}
boolean hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings = false;
for (String methodLevelPattern : methodLevelPatterns) {
if (methodLevelPattern == null) {
hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings = true;
}
else {
// controller的映射url+方法映射的url
String combinedPattern = getPathMatcher().combine(typeLevelPattern, methodLevelPattern);
// 保存到set集合中
addUrlsForPath(urls, combinedPattern);
}
}
if (hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings ||
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerType)) {
addUrlsForPath(urls, typeLevelPattern);
}
}
// 以数组形式返回controller上的所有url
return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
}
else {
// controller上的@RequestMapping映射url为空串,直接找方法的映射url
return determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, false);
}
} // controller上没@RequestMapping注解
else if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, Controller.class) != null) {
// 获取controller中方法上的映射url
return determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, false);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
到这里HandlerMapping组件就已经建立所有url和controller的对应关系。
2.根据访问url找到对应controller中处理请求的方法
下面我们开始分析第二个步骤,第二个步骤是由请求触发的,所以入口为DispatcherServlet.DispatcherServlet的核心方法为doService(),doService()中的核心逻辑由doDispatch()实现,我们查看doDispatch()的源代码。
/** 中央控制器,控制请求的转发 **/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
int interceptorIndex = -1;
try {
ModelAndView mv;
boolean errorView = false;
try {
// 1.检查是否是文件上传的请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// 2.取得处理当前请求的controller,这里也称为hanlder,处理器,第一个步骤的意义就在这里体现了.这里并不是直接返回controller,而是返回的HandlerExecutionChain请求处理器链对象,该对象封装了handler和interceptors.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
// 如果handler为空,则返回404
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//3. 获取处理request的处理器适配器handler adapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 处理 last-modified 请求头
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + requestUri + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 4.拦截器的预处理方法
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = mappedHandler.getInterceptors();
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())) {
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
return;
}
interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
// 5.实际的处理器处理请求,返回结果视图对象
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 结果视图对象的处理
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
// 6.拦截器的后处理方法
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler(), mv);
}
}
}
catch (ModelAndViewDefiningException ex) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", ex);
mv = ex.getModelAndView();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(processedRequest, response, handler, ex);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, processedRequest, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
// 请求成功响应之后的方法
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
}
第2步:getHandler(processedRequest)方法实际上就是从HandlerMapping中找到url和controller的对应关系。这也就是第一个步骤:建立Map<url,Controller>的意义。我们知道,最终处理request的是controller中的方法,我们现在只是知道了controller,还要进一步确认controller中处理request的方法。由于下面的步骤和第三个步骤关系更加紧密,直接转到第三个步骤。
3.反射调用处理请求的方法,返回结果视图
上面的方法中,第2步其实就是从第一个步骤中的Map<urls,beanName>中取得Controller,然后经过拦截器的预处理方法,到最核心的部分–第5步调用controller的方法处理请求。在第2步中我们可以知道处理request的Controller,第5步就是要根据url确定Controller中处理请求的方法,然后通过反射获取该方法上的注解和参数,解析方法和参数上的注解,最后反射调用方法获取ModelAndView结果视图。因为上面采用注解url形式说明的,所以我们这里继续以注解处理器适配器来说明。第5步调用的就是AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter的handle().handle()中的核心逻辑由invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handler)实现。
/** 获取处理请求的方法,执行并返回结果视图 **/
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// 1.获取方法解析器
ServletHandlerMethodResolver methodResolver = getMethodResolver(handler);
// 2.解析request中的url,获取处理request的方法
Method handlerMethod = methodResolver.resolveHandlerMethod(request);
// 3.方法调用器
ServletHandlerMethodInvoker methodInvoker = new ServletHandlerMethodInvoker(methodResolver);
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
ExtendedModelMap implicitModel = new BindingAwareModelMap();
// 4.执行方法
Object result = methodInvoker.invokeHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, handler, webRequest, implicitModel);
// 5.封装结果视图
ModelAndView mav =
methodInvoker.getModelAndView(handlerMethod, handler.getClass(), result, implicitModel, webRequest);
methodInvoker.updateModelAttributes(handler, (mav != null ? mav.getModel() : null), implicitModel, webRequest);
return mav;
}
这一部分的核心就在2和4了。先看第2步,通过request找controller的处理方法。实际上就是拼接controller的url和方法的url,与request的url进行匹配,找到匹配的方法。
/** 根据url获取处理请求的方法 **/
public Method resolveHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException {
// 如果请求url为,localhost:8080/springmvc/helloWorldController/say.action, 则lookupPath=helloWorldController/say.action
String lookupPath = urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
Comparator<String> pathComparator = pathMatcher.getPatternComparator(lookupPath);
Map<RequestSpecificMappingInfo, Method> targetHandlerMethods = new LinkedHashMap<RequestSpecificMappingInfo, Method>();
Set<String> allowedMethods = new LinkedHashSet<String>(7);
String resolvedMethodName = null;
// 遍历controller上的所有方法,获取url匹配的方法
for (Method handlerMethod : getHandlerMethods()) {
RequestSpecificMappingInfo mappingInfo = new RequestSpecificMappingInfo(this.mappings.get(handlerMethod));
boolean match = false;
if (mappingInfo.hasPatterns()) {// 获取方法上的url
for (String pattern : mappingInfo.getPatterns()) { // 方法上可能有多个url,springmvc支持方法映射多个url
if (!hasTypeLevelMapping() && !pattern.startsWith("/")) {
pattern = "/" + pattern;
}
// 获取controller上的映射和url和方法上的url,拼凑起来与lookupPath是否匹配
String combinedPattern = getCombinedPattern(pattern, lookupPath, request);
if (combinedPattern != null) {
if (mappingInfo.matches(request)) {
match = true;
mappingInfo.addMatchedPattern(combinedPattern);
}
else {
if (!mappingInfo.matchesRequestMethod(request)) {
allowedMethods.addAll(mappingInfo.methodNames());
}
break;
}
}
}
mappingInfo.sortMatchedPatterns(pathComparator);
}
else if (useTypeLevelMapping(request)) {
// other
}
通过上面的代码,已经可以找到处理request的Controller中的方法了,现在看如何解析该方法上的参数,并调用该方法。也就是执行方法这一步。执行方法这一步最重要的就是获取方法的参数,然后我们就可以反射调用方法了。
public final Object invokeHandlerMethod(Method handlerMethod, Object handler,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, ExtendedModelMap implicitModel) throws Exception {
Method handlerMethodToInvoke = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(handlerMethod);
try {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 处理方法上的其他注解
for (String attrName : this.methodResolver.getActualSessionAttributeNames())