一、背景介绍
Pandas在处理大数据(尤其是列比较多的场景)时,如果不做优化,内存占用还是很大的,下面通过一个实例来说明可以怎样优化
首先,生成一批18万的数据,每条数据151列
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def gen_big_data(csv_file: str, big_data_count=90000):
chars = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
dates = pd.date_range(start='2020-01-01', periods=big_data_count, freq='30s')
big_data_cols = ['Name']
for group in range(1, 31):
big_data_cols.extend([f'date str {group}',
f'bool {group}',
f'int {group}',
f'float {group}',
f'str {group}'])
big_data = []
for i in range(0, big_data_count):
row = [f'Name Item {(i + 1)}']
for _ in range(0, 30):
row.extend([str(dates[i]),
i % 2 == 0,
np.random.randint(10000, 100000),
10000 * np.random.random(),
chars[np.random.randint(0, 26)] * 15])
big_data.append(row)
df = pd.DataFrame(data=big_data, columns=big_data_cols)
df.to_csv(csv_file, index=None)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 修改存放路径以及模拟数据量(默认9万)
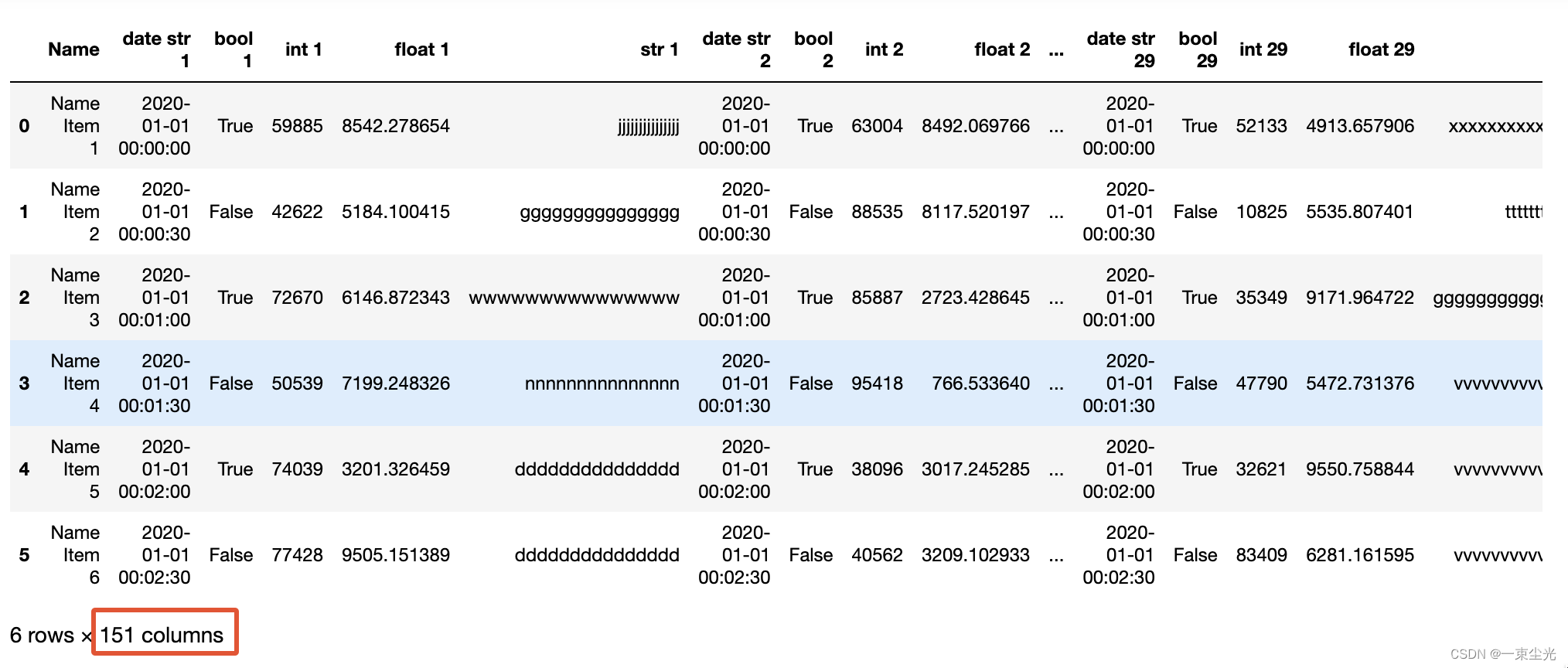
gen_big_data('./files/custom_big_data.csv', 180000)查看生成的数据格式,可以看到每一行有151列
保存数据后,先查看一下内存占用情况
import pandas as pd
def info_memory(csv_file: str):
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
print(df.info(memory_usage='deep'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
info_memory('./files/custom_big_data.csv')打印结果如下,可以看到当前内存占用为862.1MB
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 180000 entries, 0 to 179999
Columns: 151 entries, Name to str 30
dtypes: bool(30), float64(30), int64(30), object(61)
memory usage: 862.1 MB查看不同类型的内存占用情况
def info_memory_by_d_type(csv_file: str):
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
for d_type in ['bool', 'float64', 'int64', 'object']:
d_type_selected = df.select_dtypes(include=[d_type])
mem_mean_bit = d_type_selected.memory_usage(deep=True).mean()
mem_mean_mb = mem_mean_bit / 1024 ** 2
print(f'mean memory usage: {d_type:<7} - {mem_mean_mb:.3f} M')输出结果如下,其中object类型占用内存最多
mean memory usage: bool - 0.166 M
mean memory usage: float64 - 1.329 M
mean memory usage: int64 - 1.329 M
mean memory usage: object - 12.494 M二、优化方案
查看某个类型的内存占用量
def info_mem_usage_mb(pd_obj):
if isinstance(pd_obj, pd.DataFrame):
mem_usage = pd_obj.memory_usage(deep=True).sum()
else:
mem_usage = pd_obj.memory_usage(deep=True)
# 转换为MB返回
return f'{mem_usage / 1024 ** 2:02.3f} MB'int和float类型
对于int和float类型的数据,Pandas加载到内存中的数据,默认是int64和float64。一般场景下的数据,用int32和float32就足够了,用numpy.iinfo和numpy.finfo可以打印对应类型的取值范围
Machine parameters for int32
---------------------------------------------------------------
min = -2147483648
max = 2147483647
---------------------------------------------------------------
Machine parameters for int64
---------------------------------------------------------------
min = -9223372036854775808
max = 9223372036854775807
---------------------------------------------------------------Machine parameters for float32
---------------------------------------------------------------
...
maxexp = 128 max = 3.4028235e+38
nexp = 8 min = -max
---------------------------------------------------------------
Machine parameters for float64
---------------------------------------------------------------
...
maxexp = 1024 max = 1.7976931348623157e+308
nexp = 11 min = -max
---------------------------------------------------------------分别优化int和float的类型
def optimize_int_and_float():
df_int = df.select_dtypes(include=['int64'])
df_int_converted = df_int.apply(pd.to_numeric, downcast='unsigned')
df_float = df.select_dtypes(include=['float64'])
df_float_converted = df_float.apply(pd.to_numeric, downcast='float')
print('int before ', info_mem_usage_mb(df_int))
print('int converted ', info_mem_usage_mb(df_int_converted))
print('float before ', info_mem_usage_mb(df_float))
print('float converted', info_mem_usage_mb(df_float_converted))优化后的结果如下,内存减少50%左右
int before 41.199 MB
int converted 20.599 MB
float before 41.199 MB
float converted 20.599 MBobject类型中的普通str数据
获取object类型数据,并调用describe()展示统计信息
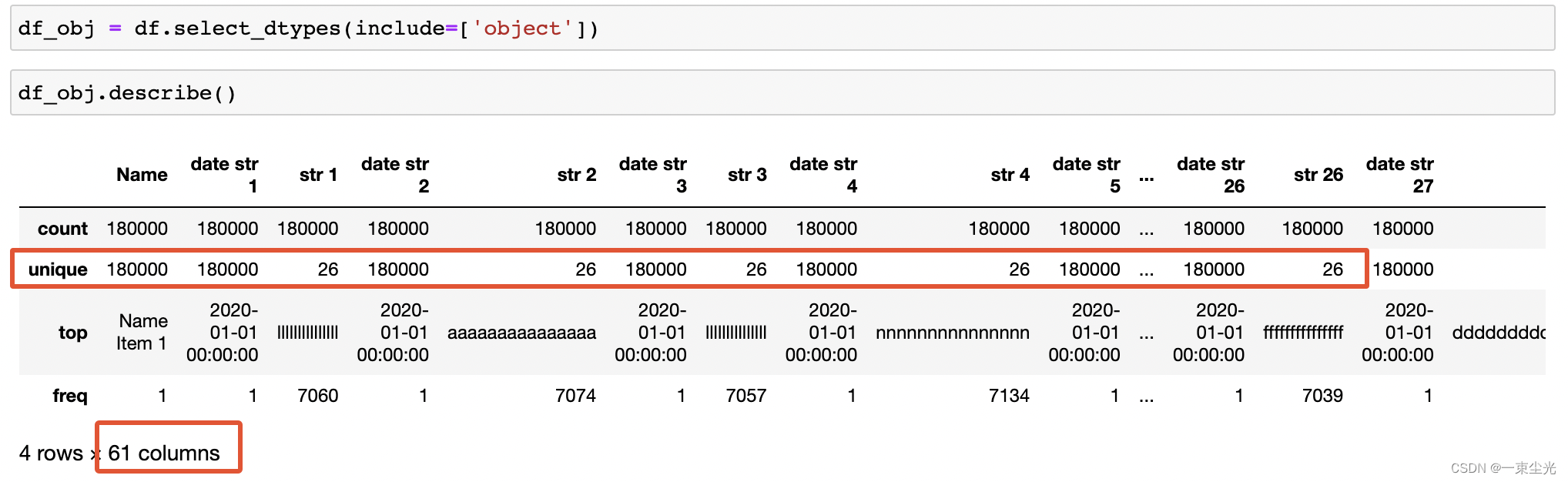
对于区分度较低的 str 1到str 30,一共只有26个可能的值,可以考虑转换为Pandas中的categroy类型,这里将区分度小于40%的列转换为category类型
def optimize_obj():
df_obj = df.select_dtypes(include=['object'])
df_obj_converted = pd.DataFrame()
for col in df_obj.columns:
unique_count = len(df_obj[col].unique())
total_count = len(df_obj[col])
# 将区分度小于40%的列转换为category类型
if unique_count / total_count <= 0.4:
df_obj_converted.loc[:, col] = df_obj[col].astype('category')
else:
df_obj_converted.loc[:, col] = df_obj[col]
print('object before ', info_mem_usage_mb(df_obj))
print('object converted', info_mem_usage_mb(self.df_obj_converted))执行结果如下,降低了300+M的内存
object before 774.602 MB
object converted 409.047 MBobject类型中的date数据
def optimize_date_str():
df_date = pd.DataFrame()
df_date_converted = pd.DataFrame()
for col_name in df.columns:
if col_name.startswith('date str'):
df_date.loc[:, col_name] = df[col_name]
df_date_converted.loc[:, col_name] = pd.to_datetime(df[col_name])
print('date before ', info_mem_usage_mb(df_date))
print('date converted', info_mem_usage_mb(df_date_converted))执行结果如下,也降低了300+M的内存
date before 391.388 MB
date converted 41.199 MB三、总体优化
综合以上的优化方法,并封装为类PandasMemoryOptimizeDemo
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
class PandasMemoryOptimizeDemo:
df: pd.DataFrame
df_int_converted: pd.DataFrame
df_float_converted: pd.DataFrame
df_obj_converted: pd.DataFrame
df_date_converted: pd.DataFrame
def __init__(self, csv_file: str):
self.csv_file = csv_file
self.df = pd.read_csv(self.csv_file)
@staticmethod
def info_mem_usage_mb(pd_obj):
if isinstance(pd_obj, pd.DataFrame):
mem_usage = pd_obj.memory_usage(deep=True).sum()
else:
mem_usage = pd_obj.memory_usage(deep=True)
# 转换为MB返回
return f'{mem_usage / 1024 ** 2:02.3f} MB'
def optimize_int_and_float(self):
df_int = self.df.select_dtypes(include=['int64'])
self.df_int_converted = df_int.apply(pd.to_numeric, downcast='unsigned')
df_float = self.df.select_dtypes(include=['float64'])
self.df_float_converted = df_float.apply(pd.to_numeric, downcast='float')
print('int before ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(df_int))
print('int converted ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(self.df_int_converted))
print('float before ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(df_float))
print('float converted', self.info_mem_usage_mb(self.df_float_converted))
def optimize_obj(self):
df_obj = self.df.select_dtypes(include=['object'])
self.df_obj_converted = pd.DataFrame()
for col in df_obj.columns:
unique_count = len(df_obj[col].unique())
total_count = len(df_obj[col])
# 将区分度小于40%的列转换为category类型
if unique_count / total_count <= 0.4:
self.df_obj_converted.loc[:, col] = df_obj[col].astype('category')
else:
self.df_obj_converted.loc[:, col] = df_obj[col]
print('object before ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(df_obj))
print('object converted', self.info_mem_usage_mb(self.df_obj_converted))
def optimize_date_str(self):
df_date = pd.DataFrame()
self.df_date_converted = pd.DataFrame()
for col_name in self.df.columns:
if col_name.startswith('date str'):
df_date.loc[:, col_name] = self.df[col_name]
self.df_date_converted.loc[:, col_name] = pd.to_datetime(self.df[col_name])
print('date before ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(df_date))
print('date converted', self.info_mem_usage_mb(self.df_date_converted))
def optimize_all(self):
self.optimize_int_and_float()
self.optimize_obj()
self.optimize_date_str()
df_converted = self.df.copy()
df_converted[self.df_int_converted.columns] = self.df_int_converted
df_converted[self.df_float_converted.columns] = self.df_float_converted
df_converted[self.df_obj_converted.columns] = self.df_obj_converted
df_converted[self.df_date_converted.columns] = self.df_date_converted
print('before ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(self.df))
print('converted', self.info_mem_usage_mb(df_converted))
if __name__ == '__main__':
optimize_demo = PandasMemoryOptimizeDemo('./files/custom_big_data.csv')
optimize_demo.optimize_all()执行结果如下,优化效果还是很明显的
before 862.149 MB
converted 105.207 MB四、直接优化read_csv方法
写代码的过程中,如果每次都按照这样的步骤,其实还是很繁琐,那能不能在调用read_csv方法时就进行优化呢?
接下来就一起来探索一下
在PyCharm中,点击read_csv进入源码,发现该方法提供了非常丰富的参数(50+),这里只列举需要的参数
def read_csv(
filepath_or_buffer: FilePath | ReadCsvBuffer[bytes] | ReadCsvBuffer[str],
# General Parsing Configuration
dtype: DtypeArg | None = None,
converters=None,
# Datetime Handling
parse_dates=None,
infer_datetime_format=False,
keep_date_col=False,
date_parser=None,
low_memory=_c_parser_defaults["low_memory"],
memory_map=False,
storage_options: StorageOptions = None,
):
# locals() should never be modified
kwds = locals().copy()可以直接指定dtype和parse_dates,最终代码如下
def big_data_optimized_read_csv(self):
d_type_dict = {}
date_indexes = []
for i in range(1, 31):
d_type_dict[f'int {i}'] = 'int32'
d_type_dict[f'float {i}'] = 'float32'
d_type_dict[f'str {i}'] = 'category'
date_indexes.append(5 * (i - 1) + 1)
self.df = pd.read_csv(self.csv_file, dtype=d_type_dict, parse_dates=date_indexes)
print('optimized read_csv: ', self.info_mem_usage_mb(self.df))执行结果如下,内存占用也大大降低了
optimized read_csv: 105.207 MB