决策树分类算法分析与实现
决策树分类算法是最为常见的一种分类算法,通过属性划分来建立一棵决策树,测试对象通过在树上由顶向下搜索确定所属的分类。决策树的构建主要需要解决两个问题:
(1)树的每次成长,选择哪个属性进行划分,可以参考下面几个标准:
A Gini系数
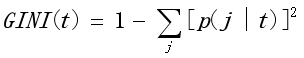
多分支Gini系数的组合方法
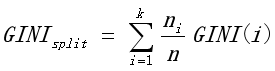
B 基于熵的信息增益或信息增益率
熵的定义
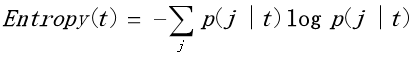
信息增益的定义
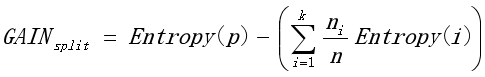
信息增益率的定义
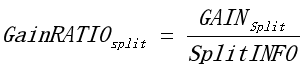
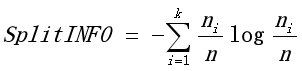
C 误分率
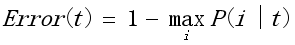
(2)什么时候在一个节点上停止生长(继续划分),可考虑包含下面两个原则:
A 当节点分配的所有记录都属于同一类时停止
B 当没有属性可以使用时停止
代码:
import numpyas np'''决策树使用方法
生成实例: clf=DecisionTree()
训练,fit(): clf.fix(X,y). X,y均为np.ndarray类型
预测,predict(): clf.predict(X)
可视化决策树,showTree()
'''classDecisionTree:def__init__(self,mode='C4.5'):
self._tree=Noneif mode=='C4.5'or mode=='ID3':
self.mode=modeelse:raise Exception('mode should be C4.5 or ID3')def_calcEntropy(self,y):"""
计算熵
:param y: 数据集的标签
:return: 熵值
"""
num=y.shape[0]
labelCounts={}for labelin y:if labelnotin labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[label]=0
labelCounts[label]+=1#计算熵
entropy=0.0for keyin labelCounts:
weight=float(labelCounts[key])/num
entropy-= weight* np.log2(weight)return entropydef_splitDataSet(self,X,y,index,value):"""
:param X: 数据集
:param y: 数据集的标签
:return: 数据集中特征下标为index,特征值等于value的子数据集
"""
ret=[]
featVec=X[:,index]
X=X[:,[ifor iinrange(X.shape[1])if i!=index]]for iinrange(len(featVec)):if featVec[i]==value:
ret.append(i)return X[ret,:],y[ret]def_chooseBestFeatureToSplit_ID3(self,X,y):"""ID3算法计算的是信息增益
对输入的数据集,选择最佳分割特征
dataSet:数据集,最后一列为label
numFeatures:特征个数
oldEntropy:原始数据集的熵
newEntropy:按某个特征分割数据集后的熵
infoGain:信息增益
bestInfoGain:记录最大的信息增益
bestFeatureIndex:信息增益最大时,所选择的分割特征的下标
"""
numFeature= X.shape[1]
oldEntropy= self._calcEntropy(y)
bestInfoGain=0.0
bestFeatureIndex=-1#对每个特征都计算一下信息增益infoGain,并用bestInfoGain记录最大的那个for iinrange(numFeature):
featList= X[:,i]
uniqueVals=set(featList)
newEntropy=0.0#对第i个特征的各个value,得到各个子数据集,计算各个子数据集的熵#进一步地可以计算得到根据第i个特征分割原始数据后的熵newEntropyfor valuein uniqueVals:
sub_X,sub_y=self._splitDataSet(X,y,i,value)
prob=len(sub_y)/float(len(y))
newEntropy+= prob* self._calcEntropy(sub_y)# 计算信息增益,根据信息增益选择最佳分割特征
infoGain= oldEntropy-newEntropyif(infoGain>bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain= infoGain
bestFeatureIndex= ireturn bestFeatureIndexdef_chooseBestFeatureToSplit_C45(self,X,y):"""C4.5算法计算的是信息增益率
"""
numFeature= X.shape[1]
oldEntropy= self._calcEntropy(y)
bestGainRatio=0.0
bestFeatureIndex=-1#对每个特征都计算一下信息增益率gainRatio=infoGain/splitInformationfor iinrange(numFeature):
featList= X[:, i]
uniqueVals=set(featList)
newEntropy=0.0
splitInformation=0.0# 对第i个特征的各个value,得到各个子数据集,计算各个子数据集的熵# 进一步地可以计算得到根据第i个特征分割原始数据后的熵newEntropyfor valuein uniqueVals:
sub_X, sub_y= self._splitDataSet(X, y, i, value)
prob=len(sub_y)/float(len(y))
newEntropy+= prob* self._calcEntropy(sub_y)
splitInformation-= prob* np.log2(prob)# 计算信息增益率,根据信息增益率选择最佳分割特征#splitInformation若为0,说明该特征的所有值都是相同的,不能作为分割特征if splitInformation==0.0:passelse:
infoGain= oldEntropy- newEntropy
gainRatio= infoGain/splitInformationif(gainRatio> bestGainRatio):
bestGainRatio= gainRatio
bestFeatureIndex= ireturn bestFeatureIndexdef_majorityCnt(self,labelList):"""返回labelList中出现次数最多的label
"""
labelCount={}for votein labelList:if votenotin labelCount.keys():
labelCount[vote]=0
labelList[vote]+=1
sortedClassCount=sorted(labelCount.items(),key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)return sortedClassCount[0][0]def_createTree(self,X,y,featureIndex):"""建立决策树
featureIndex:类型是元组,他记录了X中的特征值在原始数据中对应的下标。
"""
labelList=list(y)#所有label都相同的话,则停止分割,返回该labelif labelList.count(labelList[0])==len(labelList):return labelList[0]#没有特征可以分割时,停止分割,返回出现次数最多的labeliflen(featureIndex)==0:return self._majorityCnt(labelList)#可以继续分割的话,确定最佳分割特征if self.mode=='C4.5':
bestFeatIndex= self._chooseBestFeatureToSplit_C45(X,y)elif self.mode=='ID3':
bestFeatIndex= self._chooseBestFeatureToSplit_ID3(X,y)
bestFeatStr= featureIndex[bestFeatIndex]
featureIndex=list(featureIndex)
featureIndex.remove(bestFeatStr)
featureIndex=tuple(featureIndex)#用字典存储决策树,最佳分割特征作为key,而对应的键值仍然是一棵树(仍用字典存储)
myTree={bestFeatStr:{}}
featValues= X[:,bestFeatIndex]
uniqueVals=set(featValues)for valuein uniqueVals:#对每个value递归的创建树
sub_X,sub_y= self._splitDataSet(X,y,bestFeatIndex,value)
myTree[bestFeatStr][value]= self._createTree(sub_X,sub_y,featureIndex)return myTreedeffit(self,X,y):#类型检查ifisinstance(X,np.ndarray)andisinstance(y,np.ndarray):passelse:try:
X= np.array(X)
y= np.array(y)except:raise TypeError("numpy.ndarray required for X,y")
featureIndex=tuple(['x'+str(i)for iinrange(X.shape[1])])
self._tree= self._createTree(X,y,featureIndex)return selfdefpredict(self,X):if self._tree==None:raise NotFittedError("Estimator not fitted,call 'fit' first")# 类型检查ifisinstance(X, np.ndarray):passelse:try:
X= np.array(X)except:raise TypeError("numpy.ndarray required for X")def_classify(tree,sample):"""用训练好的决策树对输入数据分类
决策树的构建是一个递归的过程,用决策树分类也是一个递归的过程
_classify()一次只能对一个样本(sample)分类
"""
featIndex=list(tree.keys())[0]
secondDict= tree[featIndex]
key= sample[int(featIndex[1:])]
valueOfkey= secondDict[key]ifisinstance(valueOfkey,dict):
label= _classify(valueOfkey,sample)else:
label= valueOfkeyreturn labeliflen(X.shape)==1:return _classify(self._tree,X)else:
results=[]for iinrange(X.shape[0]):
results.append(_classify(self._tree,X[i]))return np.array(results)defshow(self):if self._tree==None:raise NotFittedError("Estimator not fitted,call 'fit' first")print(self._tree)
createPlot(self._tree)if __name__=='__main__':# Toy data
X=[[1,2,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0,1],[1,0,0,0,1],[2,1,1,0,1],[1,1,0,1,1]]
y=['yes','yes','no','no','no']
clf= DecisionTree(mode='ID3')
clf.fit(X, y)
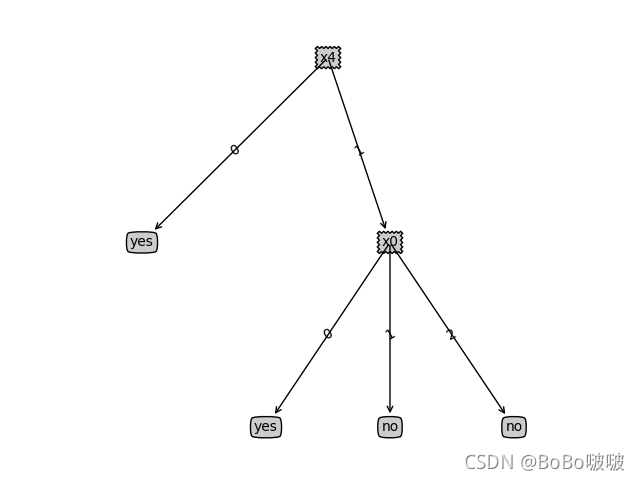
clf.show()print(clf.predict(X))# ['yes' 'yes' 'no' 'no' 'no']
clf_= DecisionTree(mode='C4.5')
clf_.fit(X, y).show()print(clf_.predict(X))# ['yes' 'yes' 'no' 'no' 'no']可视化Tree需要用到的函数
import matplotlib.pyplotas plt
decisionNode=dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode=dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args=dict(arrowstyle="<-")defgetNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs=0
firstStr=list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict= myTree[firstStr]for keyin secondDict.keys():iftype(secondDict[
key]).__name__=='dict':# test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
numLeafs+= getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])else:
numLeafs+=1return numLeafsdefgetTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth=0
firstStr=list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict= myTree[firstStr]for keyin secondDict.keys():iftype(secondDict[
key]).__name__=='dict':# test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
thisDepth=1+ getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])else:
thisDepth=1if thisDepth> maxDepth: maxDepth= thisDepthreturn maxDepthdefplotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)defplotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid=(parentPt[0]- cntrPt[0])/2.0+ cntrPt[0]
yMid=(parentPt[1]- cntrPt[1])/2.0+ cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)defplotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):# if the first key tells you what feat was split on
numLeafs= getNumLeafs(myTree)# this determines the x width of this tree# depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr=list(myTree.keys())[0]# the text label for this node should be this
cntrPt=(plotTree.xOff+(1.0+float(numLeafs))/2.0/ plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict= myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff= plotTree.yOff-1.0/ plotTree.totalDfor keyin secondDict.keys():iftype(secondDict[
key]).__name__=='dict':# test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt,str(key))# recursionelse:# it's a leaf node print the leaf node
plotTree.xOff= plotTree.xOff+1.0/ plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key],(plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt,str(key))
plotTree.yOff= plotTree.yOff+1.0/ plotTree.totalD# if you do get a dictonary you know it's a tree, and the first element will be another dictdefcreatePlot(inTree):
fig= plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops=dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1= plt.subplot(111, frameon=False,**axprops)# no ticks# createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
plotTree.totalW=float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD=float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff=-0.5/ plotTree.totalW;
plotTree.yOff=1.0;
plotTree(inTree,(0.5,1.0),'')
plt.show()结果:

使用ID3算法训练的模型,进行测试的结果
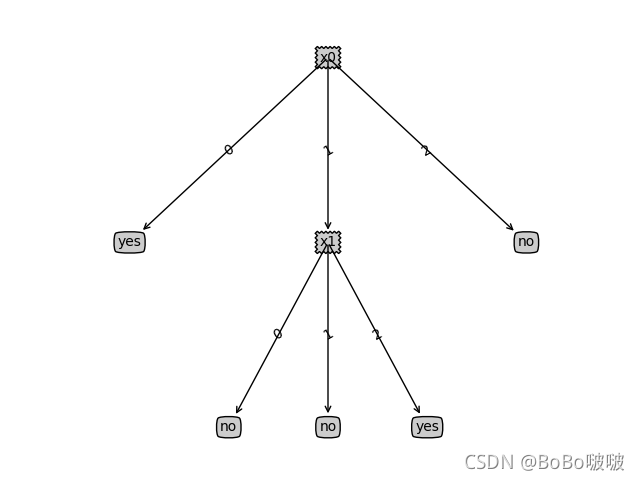
使用C4.5算法训练的模型,进行测试的结果