1.使用业务场景:
对于有的请求业务处理流程可能比较耗时,比如长查询,远程调用等,主线程会被一直占用,而tomcat线程池线程有限,处理量就会下降
servlet3.0以后提供了对异步处理的支持,springmvc封装了异步处理,满足用户请求后,主线程很快结束,并开启其它线程处理任务,并将处理结果响应用户,而主线程就可以接收更多请求。
参考官方解释:
https://spring.io/blog/2012/05/07/spring-mvc-3-2-preview-introducing-servlet-3-async-support
原理简介:
对于一次请求,比如front/test
1,springmvc开启副线程处理业务(将Callable 提交到 TaskExecutor)
2,DispatcherServlet和所有的Filter退出web容器的线程,但是response 保持打开状态
3,Callable返回结果,SpringMVC将请求front/test重新派发给容器(再重新请求一次front/test),恢复之前的处理;
4,DispatcherServlet重新被调用,将结果返回给用户
代码演示
1.这是普通的调用,我这里加了一个方法执行的时间 ,基于Rest风格的远程调用
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(){
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
String t=testInterface.test(); //远程服务调用
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
System.out.println("test程序运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程 序运行时间
return t;
}执行时间: 297ms
2.基于Callabe的调用
@RequestMapping("/test2")
public Callable<String> test2(){
Callable<String> callable= new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
String t=testInterface.test(); //远程服务调用
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
System.out.println("test2程序运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间
return t;
}
};
return callable;
}执行时间:7ms
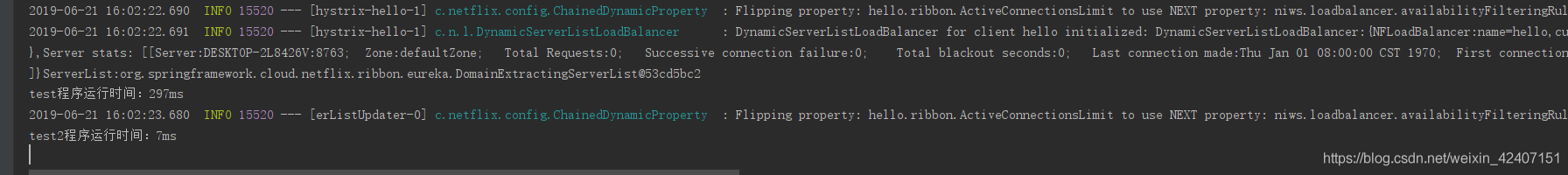
通过执行时间的对比,我们可以得出异步处理对 比如长查询,远程调用等,有一定提高系统的效率以及提高吞吐量,从而实现高并发