在写ftp上传文件至服务器的过程中,有这样一个判断:判断某个文件夹下有多少个文件,内容为null的文件不上传,所以利用BufferedReader读取文件的内容,判断是否为null,所以用到了BufferedReader.readLine(),结果竟然卡死:txt、word、Excle、Ftp文件等都没有问题,但是读取MP3、Rar、zip等文件时,就一直处于卡死状态,先看代码:
package com.test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestCh {
public void readDocFileToFtp() {
String docPath = "H:\\11"; // 文件所在路径 模拟
File file;
try {
file = new File(docPath);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if (files.length == 0) {
System.err.println(docPath + "文件夹下没有任何文件!");
} else {
Arrays.sort(files);
System.err.println("文件数---" + files.length);
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
if (files[i].isFile()) {
InputStreamReader reader;
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(files[i]));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
String message = "";
String line = "";
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取开始时间
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
message += line;
}
br.close();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取结束时间
System.out.println("程序运行时间: " + (endTime - startTime) / 1000 + "ms");
String fileName = files[i].getName();
if (message.trim() == null || message.length() == 0) {
System.err.println(fileName + "文件内容为空!");
} else {
// 上传文件
System.err.println("上传===============");
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestCh te = new TestCh();
te.readDocFileToFtp();
}
}然后一直卡死:
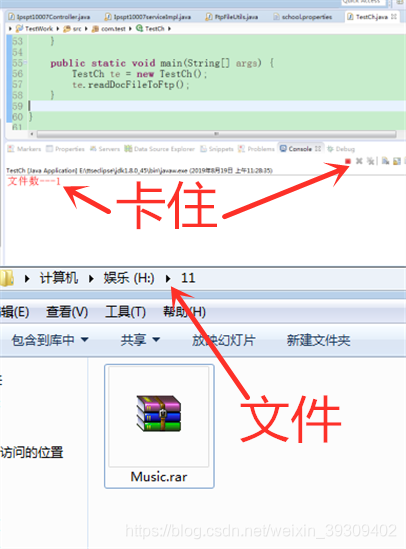
我们都知道,readLine()方法是遇到换行符或者是对应流的结束符,该方法才会认为读到了一行(才会结束其阻塞),让程序继续往下执行。但可能因为以前不留意,也没遇见过这种情况,所以就认为该方法可放心使用,今天踩了这个坑,所以做个笔记:
我们可能下意识地认为readLine()读取到没有数据时就返回null(因为read()方法当读到没有数据时返回-1),而实际上readLine()是一个阻塞函数,当没有数据读取时,就一直会阻塞在那,而不是返回null。
readLine()只有在数据流发生异常或者另一端被close()掉时,才会返回null值。
如果不指定buffer大小,则readLine()使用的buffer有8192个字符。
在达到buffer大小之前,只有遇到"/r"、"/n"、"/r/n"才会返回。
String readLine(boolean ignoreLF) throws IOException {
StringBuffer s = null;
int startChar;
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
boolean omitLF = ignoreLF || skipLF;
bufferLoop:
for (;;) {
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill(); //在此读数据
if (nextChar >= nChars) { /* EOF */
if (s != null && s.length() > 0)
return s.toString();
else
return null;
}
......//其它
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
..../其它
int n;
do {
n = in.read(cb, dst, cb.length - dst); //实质
} while (n == 0);
if (n > 0) {
nChars = dst + n;
nextChar = dst;
}
}通过查看源码可知,readLine()是调用了read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 来读取数据,后面再根据"/r"或"/n"来进行数据处理,所以使用readLine()一定要注意:
1.读入的数据要注意有/r或/n或/r/n
2.没有数据时会阻塞,在数据流异常或断开时才会返回null
3.非必要时(socket之类的数据流),要避免使用readLine(),以免为了等待一个换行/回车符而一直阻塞