Semaphore信号量概念
Semaphore信号量,一个有限的流量访问,它基于AQS共享锁实现,常常被我们用来控制多线程对有限资源的访问
Semaphore的内部类介绍
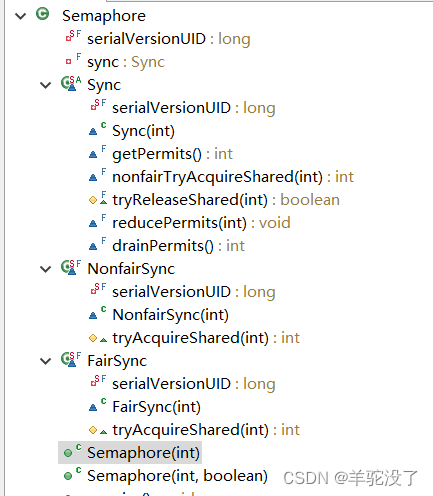
可以看到,这个类中有三个静态内部类,第一个Sync类,继承自AQS,这个类维护了Semaphore实际业务逻辑
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1192457210091910933L;
Sync(int permits) {
setState(permits);
}
final int getPermits() {
return getState();
}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
final void reducePermits(int reductions) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current - reductions;
if (next > current) // underflow
throw new Error("Permit count underflow");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return;
}
}
final int drainPermits() {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
if (current == 0 || compareAndSetState(current, 0))
return current;
}
}
}Sync有两个子类NonfairSync和FairSync
这两个类是用来做信号量的公平锁和非公平锁
可以看下这两个静态内部类的实现
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
NonfairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
//实际调用的是Sync的实现方法
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
}公平锁实现,会首先判断AQS的双向链表的是否有头结点,或者头结点是当前线程
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2014338818796000944L;
FairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
}构造器
在声明时,可以指定使用公平锁和非公平锁,并且指定信号量,这个信号量实际就是AQS中的State
/**
* Creates a {@code Semaphore} with the given number of
* permits and nonfair fairness setting.
*
* @param permits the initial number of permits available.
* This value may be negative, in which case releases
* must occur before any acquires will be granted.
*/
public Semaphore(int permits) {
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code Semaphore} with the given number of
* permits and the given fairness setting.
*
* @param permits the initial number of permits available.
* This value may be negative, in which case releases
* must occur before any acquires will be granted.
* @param fair {@code true} if this semaphore will guarantee
* first-in first-out granting of permits under contention,
* else {@code false}
*/
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}介绍完基本的信号量类,下面介绍Semaphore实现信号量资源的获取和释放
获取信号量资源
—>
调用Sync类的tryAcquireShared(1)方法—>
如果调用Semaphore类的的acquire()方法,接下来会走AQS的方法
public void acquire(int permits) throws InterruptedException {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(permits);
}调用AQS的sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(permits);
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}在方法中会判断tryAcquireShared的值,这个方法会根据是公平锁还是非公平锁,来走,应为在这两个类中都实现了这个tryAcquireShared方法,在NonfairSync中会走 这个方法,是在Sync中的
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
而在fairSync中走的是自己实现的方法
先开始一个死循环
然后通过hasQueuedPredecessors()方法来判断,是不是已经有其他线程在排队等着获取信号量了,如果是的话,为了体现先来先到的公平原则,当前线程不能去获取剩余的信号量了,直接返回-1。老老实实的排队等着
如果没有其他的线程在排队等着获取信号量,那么就接着执行后面的逻辑
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
}如果tryAcquireShared返回值小于0,代表已经没有信号量可以获取了,
则调用AQS的doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(1)方法,将当前线程加入到同步队列中阻塞
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}释放信号量
—>调用Sync类的tryReleaseShared(1)方法—>如果tryReleaseShared返回值为true,代表成功释放了一个信号量,则调用AQS的doReleaseShared()方法,唤醒同步队列中head节点的后继节点线程
调用Semaphore类的release方法 ,然后调用AQS的releaseShared方法
public void release(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.releaseShared(permits);
}在AQS中会调用tryRealaseShared()方法 ,这个方法是在 Sync中实现的方法
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}这个方法是这样写的,大概意思是
死循环中获得当前信号量,将当前的信号值加上要释放的releases值,之后cas设置state,如果修改成功,返回true
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}最后再执行AQS的方法doReleaseShared()方法
/**
* Release action for shared mode -- signals successor and ensures
* propagation. (Note: For exclusive mode, release just amounts
* to calling unparkSuccessor of head if it needs signal.)
*/
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}