文章目录
Annotation工作方式
从Java5.0版发布以来,5.0平台提供了一个正式的annoatation功能:允许开发者定义、使用自己的annotation类型。此功能由一个定义annotation声明的语法,读取annotation的API,一个使用annotation修饰的class文件,一个annotation处理工具(apt)组成。
annotation并不直接影响代码语义,但是它能够工作的方式被看作类似程序的工具或者类库,它会反过来对正在运行的程序语义有所影响。
annotation可以从源文件、class文件或者以在运行时反射的多种方式被读取。
JDK5 内建Annotation
Java 注解(Annotation):
限定Override父类方法@Override
java.langOverride是个Marker annotation
用于标示的Annotation,Annotation名称本身即表示了要给工具程序的信息
a) Override 注解表示子类要重写(override) 父类的对应方法。
package sixtyNineth;publicclassOverrideTest{@Overridepublic StringtoString(){return"This is OverrideTest";}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
OverrideTest test=newOverrideTest();
System.out.println(test);}}结果是:
This is OverrideTest
标示方法为Deprecated @Deprectated
对编译程序说明某个方法已经不建议使用,即该方法是过时的。
java.lang.Deprecated也是个Marker annotation
Deprecated这个名称在告知编译程序,被@Deprecated标示的方法是一个不建议被使用的方法
b) Deprecated 注解表示方法是不建议被使用的。
package sixtyNineth;import java.sql.Date;publicclassDeprecatedTest{@DeprecatedpublicvoiddoSomething(){
System.out.println("do something");}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
DeprecatedTest test=newDeprecatedTest();
test.doSomething();/*Date date = new Date(0);
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());*/}}结果是:
do something
抑制编译程序警告@SuppressWarnings
对编译程序说明某个方法中若有警告讯息,则加以抑制
c) SuppressWarnings 注解表示抑制警告。
package sixtyNineth;import java.util.Date;import java.util.Map;import java.util.TreeMap;publicclassSuppressWarningTest{@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked","rawtypes"})publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
Map map=newTreeMap();
map.put("hello",newDate());
System.out.println(map.get("hello"));}}结果是:
Sun Jan 13 19:59:06 CST 2019
自定义Annotation类型
定义Marker Annotation,也就是Annotation名称本身即提供信息对于程序分析工具来说,主要是检查是否有Marker Annotation的出现,并作出对应的动作。
自定义注解:当注解中的属性名为 value 时,在对其赋值时可以不指定属性的名称
而直接写上属性值即可;除了 value 以外的其他值都需要使用 name=value 这种赋值
方式,即明确指定给谁赋值。
package sixtyNineth;public @interfaceAnnotationTest{
Stringvalue1();}package sixtyNineth;public @interfaceAnnotationTest1{
Stringvalue();}package sixtyNineth;@AnnotationTest(value1="hello")publicclassAnnotationUsage{@AnnotationTest1("world")publicvoidmethod(){
System.out.println("usage of annotation");}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
AnnotationUsage usage=newAnnotationUsage();
usage.method();}}结果是:
usage of annotation
Single-value annotation
value成员设定默认值,用"default"关键词
数组方式的使用
枚举在Annotation中的应用
package sixtyNineth;public @interfaceAnnotationTest1{
String[]value1()default"hello";
EnumTestvalue2();}enum EnumTest{
Hello, World, Welcome}package sixtyNineth;@AnnotationTest1(value2= EnumTest.Welcome, value1="world")publicclassAnnotationUsage{@AnnotationTest1(value1={"hello","haha"}, value2= EnumTest.Hello)publicvoidmethod(){
System.out.println("usage of annotation");}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
AnnotationUsage usage=newAnnotationUsage();
usage.method();}}使用@interface自定义Annotation型态时,实际上是自动继承了java.lang.annotation.Annnotation接口由编译程序自动为您完成其它产生的细节,在定义Annotation型态时,不能继承其他的Annotation型态或者接口。
java.lang.annotation
Interface Annotation
The common interface extended by all annotation types. Note that an interface that manually extends this one does not define an annotation type. Also note that this interface does not itself define an annotation type.
当 我 们 使 用 @interface 关 键 字 定 义 一 个 注 解 时 , 该 注 解 隐 含 地 继 承 了java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口;如果我们定义了一个接口,并且让该接口继承自 Annotation,那么我们所定义的接口依然还是接口而不是注解; Annotation 本身是接口而不是注解。 (可以与 Enum 类比。)
定义Annotation型态时也可以使用包来管理类别方式类同于类的导入功能。
告知编译程序如何处理@Retention
java.lang.annotation.Retention型态可以在您定义Annotation型态时,指示编译程序该如何对待您的自定义的Annotation型态。
==预设上编译程序会将Annotation信息留在.class档案中,==但是不被虚拟机读取,而仅用于编译程序或工具程序运行时提供信息。
在使用Retention型态时,需要提供java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy的枚举型态Package java.lang.annotation;
publicenum RetentionPolicy{
SOURCE,//编译程序处理完Annotation信息后就完成任务
CLASS,//编译程序将Annotation储存于class档中,缺省,不由VM读入
RUNTIME//编译程序将Annotation储存于class档中,可由VM读入,通过反射的方式读取到}RetentionPolicy为SOURCE的例子是@SuppressWarnings
仅在编译时期告知编译程序来抑制警告,所以不必将这个信息储存于.class档案
RetentionPolicy为RUNTIME的时机,可以像是您使用Java设计一个程序代码分析工具,您让VM能读出Annotation信息,以便在分析程序时使用。
搭配反射(Reflectiong)机制,就可以达到这个目的
package Seventieth.First;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)public @interfaceMyAnnotation{
Stringhello()default"Matthew";
Stringworld();}package Seventieth.First;@MyAnnotation(hello="beijing", world="shanghai")publicclassMyTest{@MyAnnotation(hello="tianjing", world="shangdi")@Deprecated@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")publicvoidoutput(){
System.out.println("output something");}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
MyTest myTest=newMyTest();
myTest.output();}}java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement接口
public Annotation getAnnotation(Class annotationType);
public Annotation[] getAnnotations();
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations();
public boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class annotationType);
Class、Constructor、Field、Method、Package等类别,都实现了AnnotationElement接口
package Seventieth.First;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String hello() default "Matthew";
String world();
}package Seventieth.First;@MyAnnotation(hello="beijing", world="shanghai")publicclassMyTest{@MyAnnotation(hello="tianjing", world="shangdi")@Deprecated@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")publicvoidoutput(){
System.out.println("output something");}/* public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTest myTest = new MyTest();
myTest.output();
}*/}package Seventieth.First;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MyReflection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
MyTest myTest = new MyTest();
Class<MyTest> c = MyTest.class;
Method method = c.getMethod("output", new Class[]{});
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){
method.invoke(myTest, new Object[]{});
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
String hello = myAnnotation.hello();
String world = myAnnotation.world();
System.out.println(hello + "," + world);
}
Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation annotation : annotations){
System.out.println(annotation.annotationType().getName());
}
}
}结果是:
output something
tianjing,shangdi
Seventieth.First.MyAnnotation
java.lang.Deprecated
当我们在@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)不用RUNTIME而用CLASS和SOURCE时,运行结果为空,因为注解存在了class文件当中,但是,VM不会反射读取出来,method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)为false所以没有输出。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
因为SuppressWarnings的RetentionPolicy为SOURCE
限定annotation使用对象@Target
使用java.lang.annotation.Target可以定义其使用的时机,在定义时要指定java.lang.annotation.ElementType的枚举值之一
package java.lang.annotation;
public enum ElementType{
TYPE,//适用class,interface,enum
FIELD,//适用field
METHOD,//适用method
PARAMETER,//适用method上的parameter
CONSTRUCTOR,//适用costructor
LOCAL_VARIABLE,//适用局部变量
ABBOTATION_TYPE,//适用annotation型态
PACKAGE//适用package
}
package Seventieth.First;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.METHOD)public @interfaceMyTarget{
Stringvalue();}package Seventieth.First;publicclassMyTargetTest{@MyTarget("hello")publicvoiddoSomething(){
System.out.println("hello world");}}如果把 @MyTarget(“hello”)放在类上面就会报错’@MyTarget’ not applicable to type,我们把
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)改为@Target(ElementType.TYPE)就不会报错了
要求为API文件@Documented
想要在使用者制作JavaDoc文件的同时,也一并将Annotation的讯息加入至API文件中使用java.lang.annotation.Documented
package Seventieth.First;
public @interface DocumentedAnnotation {
String hello();
}package Seventieth.First;
public class DocumentedTest {
@DocumentedAnnotation(hello = "welcome")
public void method(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}生成java帮助文档在Tool》Generate JavaDoc
然后在弹出的界面点击Output directory后的按钮选择文档生成路径
接下来在底部的Locale输入框配置语言和编码集,如下图所示,语言用zh_CN,代表中文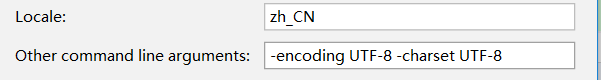
点击ok生成帮助文档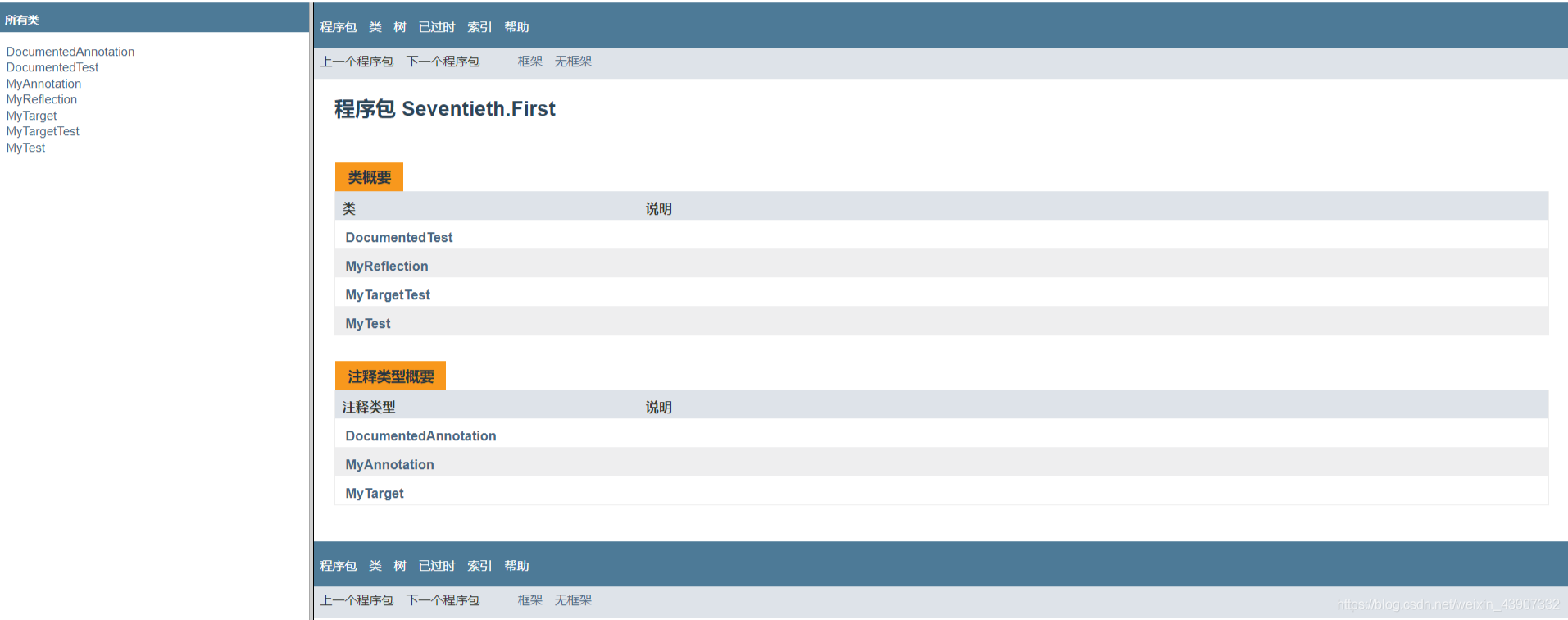
这就是我生成的java帮助文档,点击DocumentTest拉到最下面有方法详细资料
我们将DoucumentedAnnotation.java更改一下
package Seventieth.First;import java.lang.annotation.Documented;@Documentedpublic @interfaceDocumentedAnnotation{
Stringhello();}再次生成帮助文档,我们发现发发详细资料变成如下图所示的样子

子类是否继承父类@Inherited
预设上夫类别中断Annotation并不会被继承至子类别中,可以在定义Annotation型态时加上java.lang.annotation.Inherited型态的Annotation
通过JUnit深入理解反射与注解的使用方式与场景
现在项目中导入jar包
package Seventieth.Secound;import junit.framework.TestCase;publicclassTestextendsTestCase{publicvoidtestAdd(){
System.out.println("hello world");}publicvoidtestSubtract(){
System.out.println("welcome");}}结果是:
hello world
welcome
方法必须以test开头,JUnit我们学过反射后应该大致了解其思路,首先获得这个类的Class对象,然后获得其所有的方法,存入Method[]然后遍历每一个方法,getName获得方法名,如果是以test开头就通过method.invoke执行这个方法
JUnit(3.8、 4.x): Keep the bar green to keep the code clean.
package Seventieth.Secound;import org.junit.Test;publicclassTest2{@Testpublicvoidhello(){
System.out.println("hello world");}}JUnit4 的执行的一般流程:
a) 首先获得待测试类所对应的 Class 对象。
b) 然后通过该 Class 对象获得当前类中所有 public 方法所对应的 Method 数组。
c) 遍历该 Method 数组,取得每一个 Method 对象
d) 调用每个 Method 对象的 isAnnotationPresent(Test.class)方法,判断该方法是否被 Test
注解所修饰。
e) 如果该方法返回 true,那么调用 method.invoke()方法去执行该方法,否则不执行。
单元测试不是为了证明你是对的,而是证明你没有错误。
Writing Secure Code(编写安全的代码): Input is evil。