点击上方 "程序员小乐"关注, 星标或置顶一起成长
每天凌晨00点00分, 第一时间与你相约
每日英文
There are times that it is better to let things happen,rather than insisting on how you want them to be done.
有时候,最好让事情顺其自然,而不是坚持按你的想法去做。
每日掏心话
请记住,别在生气的时候做决定,别在开心的时候说承诺。
来自:阿进的写字台 | 责编:乐乐
链接:cnblogs.com/homejim/p/9853703.html
程序员小乐(ID:study_tech)第 992 次推文 图源:百度
往日回顾:如何让你的Nginx 提升10倍性能?
正文
在select 语句中查询得到的是一张二维表, 水平方向上看是一个个字段, 垂直方向上看是一条条记录。作为面向对象的语言,Java 中的的对象是根据类定义创建的。类之间的引用关系可以认为是嵌套的关系。
在 mybatis 中,resultMap 节点定义了结果集和结果对象(JavaBean)之间的映射规则。
本文主要讲解的是resultMap 的解析。
两个基础类
在阅读本文之前, 最好能对这两个类有相应的理解。
1.1、列映射类ResultMapping
ResultMapping 对象记录了结果集中一列与队友JavaBean中一个属性的对应关系。
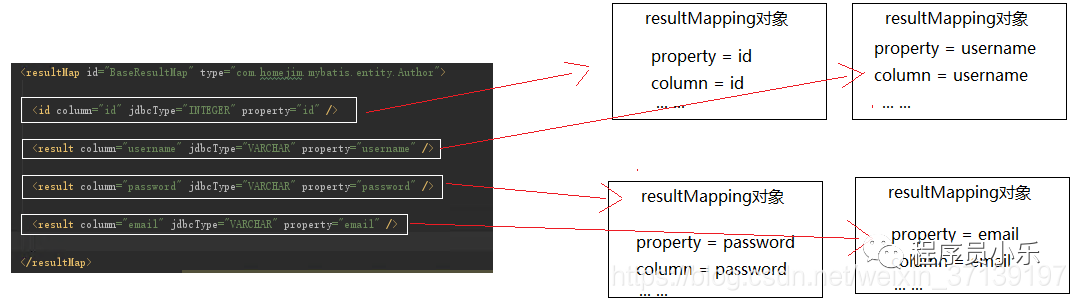
更多详情, 请参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/homejim/p/9833863.html
1.2、结果集映射类ResultMap
ResultMap 对应的是结果集 中的一个结果集。其基本组成部分中, 含有 ResultMapping 对象。
其组成大致如下:
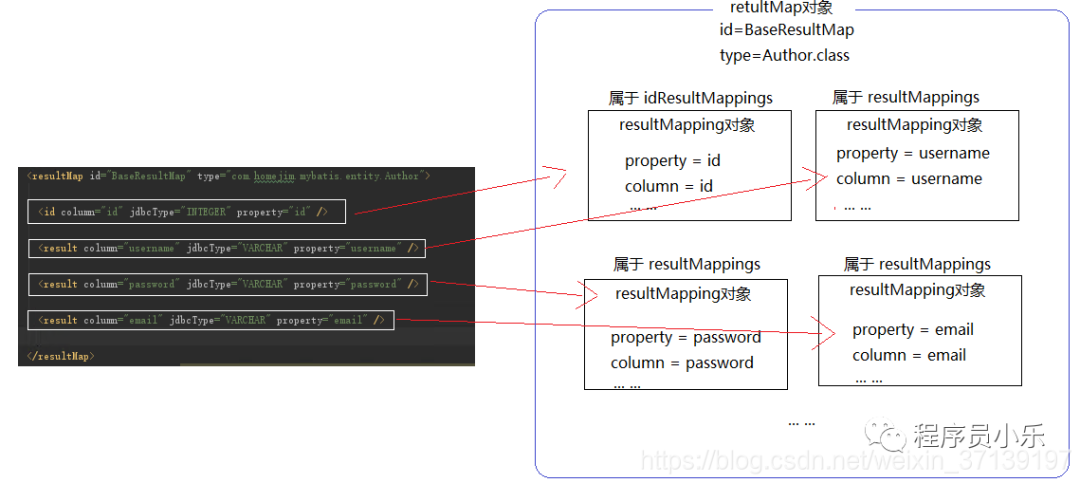
更多详情, 请参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/homejim/p/9840373.html
解析
2.1、入口函数
resultMap 是mapper.xml 文件下的, 因此其是解析Mapper 的一个环节。
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));解析, 由于是可以有多个的, 因此, context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap")返回的是一个 List。
private void resultMapElements(List<XNode> list) throws Exception {
// 遍历, 解析
for (XNode resultMapNode : list) {
try {
resultMapElement(resultMapNode);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// ignore, it will be retried
}
}
}2.2、整个过程就是 resultMapElement 这个函数。
其流程大体如下:
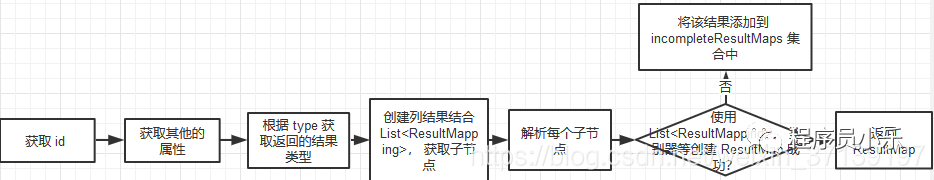
对应的代码
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode) throws Exception {
return resultMapElement(resultMapNode, Collections.<ResultMapping> emptyList());
}
/**
* 处理 <resultMap> 节点, 将节点解析成 ResultMap 对象, 下面包含有 ResultMapping 对象组成的列表
* @param resultMapNode resultMap 节点
* @param additionalResultMappings 另外的 ResultMapping 列
* @return ResultMap 对象
* @throws Exception
*/
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取 ID , 默认值会拼装所有父节点的 id 或 value 或 property
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
// 获取 type 属性, 表示结果集将被映射为 type 指定类型的对象
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// 获取 extends 属性, 其表示结果集的继承
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
// 自动映射属性。 将列名自动映射为属性
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
// 解析 type, 获取其类型
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
Discriminator discriminator = null;
// 记录解析的结果
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
// 处理子节点
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
// 处理 constructor 节点
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析构造函数元素,其下的没每一个子节点都会生产一个 ResultMapping 对象
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
// 处理 discriminator 节点
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
// 处理其余节点, 如 id, result, assosation d等
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
// 创建 resultMapping 对象, 并添加到 resultMappings 中
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
// 创建 ResultMapResolver 对象, 该对象可以生成 ResultMap 对象
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 如果无法创建 ResultMap 对象, 则将该结果添加到 incompleteResultMaps 集合中
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}2.3、获取 id
id 对于 resultMap 来说是很重要的, 它是一个身份标识。具有唯一性
搜索公众号程序员小乐回复关键字“Java”获取Java面试题和答案。
// 获取 ID , 默认值会拼装所有父节点的 id 或 value 或 property。
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id", resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());这里涉及到XNode 对象中的两个函数
public String getStringAttribute(String name, String def) {
String value = attributes.getProperty(name);
if (value == null) {
return def;
} else {
return value;
}
}该函数是获取XNode 对象对应XML 节点的name 属性值, 如果该属性不存在, 则返回传入的默认值 def。
而在获取 id 的过程中, 默认值是下面这个函数
/**
* 生成元素节点的基础 id
* @return
*/
public String getValueBasedIdentifier() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
XNode current = this;
// 当前的节点不为空
while (current != null) {
// 如果节点不等于 this, 则在0之前插入 _ 符号, 因为是不断的获取父节点的, 因此是插在前面
if (current != this) {
builder.insert(0, "_");
}
// 获取 id, id不存在则获取value, value不存在则获取 property。
String value = current.getStringAttribute("id",
current.getStringAttribute("value",
current.getStringAttribute("property", null)));
// value 非空, 则将.替换为_, 并将value的值加上 []
if (value != null) {
value = value.replace('.', '_');
builder.insert(0, "]");
builder.insert(0,
value);
builder.insert(0, "[");
}
// 不管 value 是否存在, 前面都添加上节点的名称
builder.insert(0, current.getName());
// 获取父节点
current = current.getParent();
}
return builder.toString();
}该函数是生成元素节点的id, 如果是这样子的 XML。
<employee id="${id_var}">
<blah something="that"/>
<first_name>Jim</first_name>
<last_name>Smith</last_name>
<birth_date>
<year>1970</year>
<month>6</month>
<day>15</day>
</birth_date>
<height units="ft">5.8</height>
<weight units="lbs">200</weight>
<active>true</active>
</employee>我们调用
XNode node = parser.evalNode("/employee/height");
node.getValueBasedIdentifier();则, 返回值应该是
employee[${id_var}]_height2.4、解析结果集的类型
结果集的类型, 对应的是一个JavaBean 对象。通过反射来获得该类型。
// 获取type, type 不存在则获取 ofType, ofType
// 不存在则获取 resultType, resultType 不存在则获取 javaType
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
// ... ...
// 获取 type 对应的 Class 对象
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);看源码, 有很多个 def 值, 也就是说, 我们在配置结果集的类型的时候都是有优先级的。但是, 这里有一个奇怪的地方, 我源代码版本(3.5.0-SNAPSHOT)的 的属性, 只有 type, 没有 ofType/resultType/javaType。以下为相应的 DTD 约束:
<!ELEMENT resultMap (constructor?,id*,result*,association*,collection*, discriminator?)>
<!ATTLIST resultMap
id CDATA #REQUIRED
type CDATA #REQUIRED
extends CDATA #IMPLIED
autoMapping (true|false) #IMPLIED>我怀疑是兼容以前的版本。
2.5、获取继承结果集和自动映射
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");这个两个属性都是在配置XML 的时候可有可无的。
2.6、解析
先看 DTD 约束
<!ELEMENT resultMap (constructor?,id*,result*,association*,collection*, discriminator?)>可以有以下几个子节点:
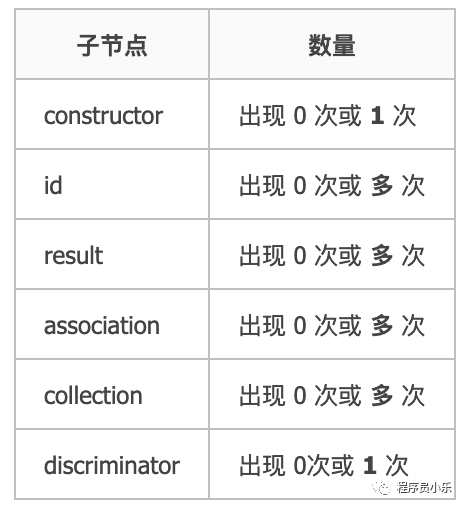
子节点解析过程很简单
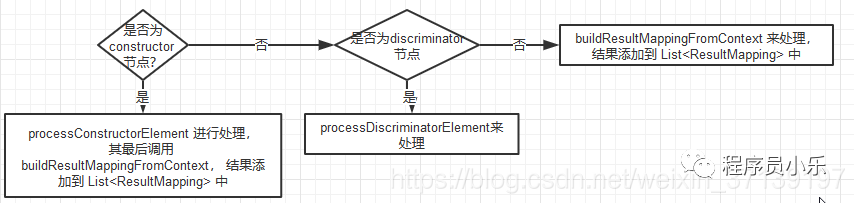
根据类型进行解析, 最后获得 resultMappings
// 创建一个 resultMappings 的链表
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
// 将从其他地方传入的additionalResultMappings添加到该链表中
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
// 获取子节点
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
// 遍历解析子节点
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析构造函数元素,其下的没每一个子节点都会生产一个 ResultMapping 对象
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
// 解析 discriminator 节点
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
// 解析其余的节点
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}除了discriminator 节点, 其余节点最后都会回到 buildResultMappingFromContext 方法上, 该方法是创建ResultMapping 对象。
/**
* 获取一行, 如result等, 取得他们所有的属性, 通过这些属性建立 `ResultMapping` 对象
* @param context 对于节点本身
* @param resultType resultMap 的结果类型
* @param flags flag 属性, 对应 ResultFlag 枚举中的属性。 一般情况下为空
* @return 返回 ResultMapping
* @throws Exception
*/
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception {
String property;
// 获取节点的属性, 如果节点是构造函数(只有name属性, 没有property),
// 则获取的是 name, 否则获取 property
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
// 获取嵌套的结果集
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap",
processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.<ResultMapping> emptyList()));
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
// 以上获取各个属性节点
// 解析 javaType, typeHandler, jdbcType
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 创建resultMapping对象
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect, nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
}如果是discriminator, 则处理该元素并创建鉴别器。
/**
* 处理鉴别器
* @param context 节点
* @param resultType 结果类型
* @param resultMappings 列结果集合
* @return 鉴别器
* @throws Exception
*/
private Discriminator processDiscriminatorElement(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
// 先获取各个属性
// 取得 javaType 对应的类型
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
// 取得 typeHandler 对应的类型
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = (Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>>) resolveClass(typeHandler);
// 取得 jdbcType 对应的类型
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
// 创建 discriminatorMap, 并遍历子节点, 以 value->resultMap 的方式放入discriminatorMap中
Map<String, String> discriminatorMap = new HashMap<>();
for (XNode caseChild : context.getChildren()) {
String value = caseChild.getStringAttribute("value");
String resultMap = caseChild.getStringAttribute("resultMap", processNestedResultMappings(caseChild, resultMappings));
discriminatorMap.put(value, resultMap);
}
// 创建鉴别器
return builderAssistant.buildDiscriminator(resultType, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, typeHandlerClass, discriminatorMap);
}鉴别器内部, 也是含有ResultMapping 的
public class Discriminator {
private ResultMapping resultMapping;
private Map<String, String> discriminatorMap;
......
}2.7、创建 ResultMap 对象
在解析完 的各个属性和子节点之后。创建 ResultMapResolver 对象, 通过对象可以生成 ResultMap。
搜索公众号程序员小乐回复关键字“offer”获取算法面试题和答案。
/**
* 创建并添加 ResultMap 到 Configuration 对象中
* @param id id, 配置了 id 可以提高效率
* @param type 类型
* @param extend 继承
* @param discriminator 鉴别器
* @param resultMappings 列集
* @param autoMapping 是否自动映射
* @return 返回创建的 ResultMap 对象
*/
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id,
Class<?> type,
String extend,
Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings,
Boolean autoMapping) {
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
if (extend != null) {
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
// 从 configuration 中获取继承的结果集
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
// 获取所集成结果集的所有 ResultMapping 集合
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
// 移除需要覆盖的 ResultMapping 集合
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
// 如果该 resultMap 中定义了构造节点, 则移除其父节点的构造器
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
if (declaresConstructor) {
Iterator<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappingsIter = extendedResultMappings.iterator();
while (extendedResultMappingsIter.hasNext()) {
if (extendedResultMappingsIter.next().getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
extendedResultMappingsIter.remove();
}
}
}
// 添加需要被继承的 ResultMapping 集合
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 通过建造者模式创建 ResultMap 对象
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
// 添加到 Configuration 对象中
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}解析结果
有如下的数据库表
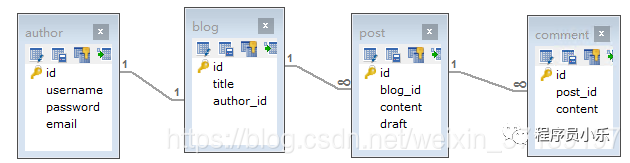
通过代码生成器生成 XML 和 Mapper。
添加结果集

对应的 sql

则最后解析出的结果
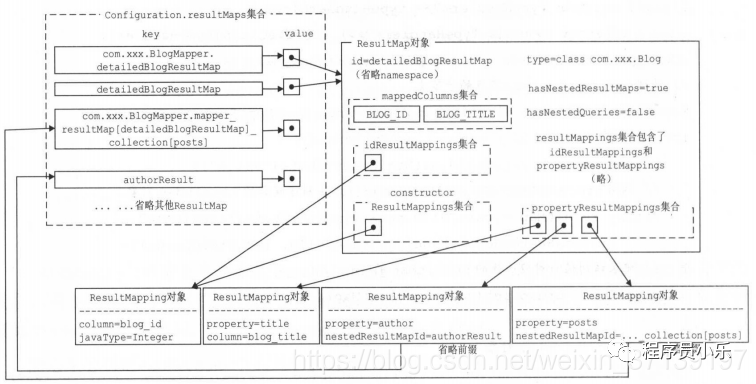
使用示例
https://github.com/homejim/mybatis-cn
欢迎在留言区留下你的观点,一起讨论提高。如果今天的文章让你有新的启发,欢迎转发分享给更多人。欢迎加入程序员小乐技术交流群,在后台回复“加群”或者“学习”即可。
猜你还想看
面试官问我:介绍一下 MyBatis 事务?我竟然回答不上来...
API 接口设计之 token、timestamp、sign 具体架构与实现
关注订阅号「程序员小乐」,收看更多精彩内容