前后端分离项目中后端开发需要写相应的接口,定义统一的返回格式有利于提高开发效率和沟通的成本。通常返回的格式主要如下两种:
1. 只返回相应的状态,格式如下:
{
"code": "200",
"msg": "SUCCESS"
}2. 返回相应的状态及数据,格式如下:
{
"code": "200",
"msg": "查询成功",
"result": {
"id": 10,
"name": "张三",
"emil": "1234456@qq.com",
"phone": null,
"address": "测试地址"
}
} 状态代码定义如下:
code : 请求处理状态
- 200: 请求处理成功
- 400: 请求处理失败
- 500: 服务器内部错误
- 401未认证(签名错误)
- 404接口不存在
Springboot中我们可以使用泛型来定义统一的返回结果:
1. 先定义只返回状态的Result
package com.example.demo.base;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class Result {
private String code;
private String msg;
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return JSON.toJSONString(this);
}
}定义即有数据又有返回状态的DateResult
package com.example.demo.base;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class DateResult<T> extends Result implements Serializable {
private T result;
public T getResult() {
return (T) result;
}
public void setResult(T result) {
this.result = result;
}
}定义响应码枚举
package com.example.demo.base;
/**
* 响应码枚举
*/
public enum ResultCode {
SUCCESS("200"), //成功
FAIL("400"), //失败
UNAUTHORIZED("401"), //未认证(签名错误)
NOT_FOUND("404"), //接口不存在
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR("500");//服务器内部错误
private final String code;
ResultCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String code() {
return code;
}
}在Controller类中使用方法如下:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.demo.base.DateResult;
import com.example.demo.base.Result;
import com.example.demo.base.ResultCode;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/update")
public Result updateUser(@RequestParam Integer id) {
Result result = new Result();
//相应的逻辑更新逻辑......... 假如更新成功
result.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS.code());
result.setMsg("更新成功");
return result;
}
@RequestMapping("/detail")
public DateResult<User> queryUser(@RequestParam Integer id) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(10);
user.setName("张三");
user.setEmil("1234456@qq.com");
user.setAddress("测试地址");
DateResult<User> dateResult = new DateResult<User>();
dateResult.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS.code());
dateResult.setMsg("查询成功");
dateResult.setResult(user);
return dateResult;
}
}实体类User代码如下:
package com.example.demo.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String emil;
private String phone;
private String address;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmil() {
return emil;
}
public void setEmil(String emil) {
this.emil = emil;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return JSON.toJSONString(this);
}
}先测试没有数据的返回格式,测试结果如下:
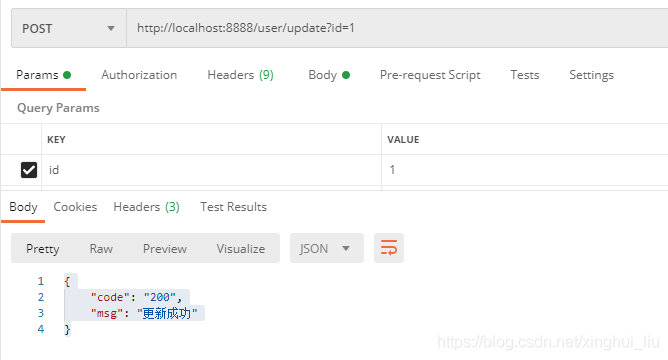
测试有返回数据的格式,测试结果如下:
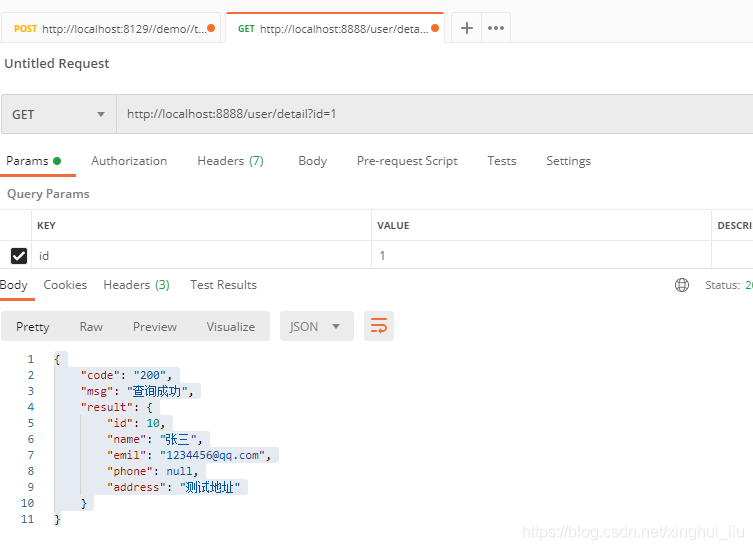
如上的返回结果,我们需要在controller类中每次都需要new一个返回对象比较麻烦,我们可以新建一个ResultUtil
package com.example.demo.base;
/**
* 响应结果生成工具
*/
public class ResultUtil {
private static final String DEFAULT_SUCCESS_MESSAGE = "SUCCESS";
public static Result genSuccessResult() {
Result result = new Result();
result.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS.code());
result.setMsg(DEFAULT_SUCCESS_MESSAGE);
return result;
}
public static <T> DateResult<T> genSuccessResult(T data) {
DateResult<T> dateResult = new DateResult<T>();
dateResult.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS.code());
dateResult.setMsg(DEFAULT_SUCCESS_MESSAGE);
dateResult.setResult(data);
return dateResult;
}
}controller 类的代码修改如下:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.demo.base.DateResult;
import com.example.demo.base.Result;
import com.example.demo.base.ResultUtil;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/update")
public Result updateUser(@RequestParam Integer id) {
return ResultUtil.genSuccessResult();
}
@RequestMapping("/detail")
public DateResult<User> queryUser(@RequestParam Integer id) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(10);
user.setName("张三");
user.setEmil("1234456@qq.com");
user.setAddress("测试地址");
return ResultUtil.genSuccessResult(user);
}
}