public class Node1<K,V> {
int hash;
K key;
V value;
Node1 next;
}
public class HashMapTest01 <K,V>{
Node1[] table; //位桶数组,bucket array
int size; //存放键值对的个数
public HashMapTest01(){
table =new Node1[16]; //长度定义为2的整数幂
}
public static int myHash(int v,int length){
// System.out.println("hash in myHash:"+(v&(length-1)));//直接位运算,效率高
// System.out.println("hash in myHash:"+(v%(length-1)));//取模运算,效率低
return v&(length-1); //返回哈希值
}
public void put(K key,V value) {
//定义了新的结点对象
Node1 newNode1 = new Node1();
newNode1.hash = myHash(key.hashCode(), table.length);
newNode1.value = value;
newNode1.key=key;
newNode1.next = null;
Node1 temp = table[newNode1.hash];
Node1 iterLast=null;
boolean keyRepeat=false;
if (temp == null) { //此处数组元素为空 则直接把新结点放进去
table[newNode1.hash] = newNode1;
size++;
} else {//如果此处数组元素不为空,则遍历对应的链表
//遍历对应的链表
while (temp != null) {
//判断key如果重复则覆盖
if (temp.key!=null&&temp.key.equals(key)) {
keyRepeat=true;
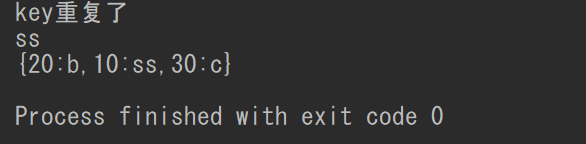
System.out.println("key重复了");
temp.value=value;//覆盖value
break;
} else {
//key不重复则遍历下一个
iterLast=temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
}
if(keyRepeat==false){ //如果没有发生key重复的情况则加到链表最后面
iterLast.next = newNode1;
size++;
}
}
}
public V get(K key){
//根据hashcode值获得对应的数组然后进行比较 找到相应的Key值
int hash=myHash(key.hashCode(),table.length);
V value=null;
if(table[hash]==null){
return null;
}else{
Node1 temp=table[hash];
while(temp!=null){
if(temp.key.equals(key)){//如果相等则说明找到了键值对,返回相应的结点
value=(V)temp.value;
break;
}else{
temp=temp.next;
}
}
}
return value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
//{10:aa,20bb}
//核心思想 先遍历数组再遍历结点
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("{");
for(int i=0;i<table.length;i++){
Node1 temp=table[i];
while(temp!=null){
sb.append(temp.key+":"+temp.value+",");
temp=temp.next;
}
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length()-1,'}');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMapTest01<Integer,String> m=new HashMapTest01<>();
m.put(10,"a");
m.put(20,"b");
m.put(30,"c");
m.put(10,"ss");
System.out.println(m.get(10));
System.out.println(m);
// for(int i=10;i<100;i++){//测试哈希冲突
// System.out.println(i+"-----"+myHash(i,16));
// }
// System.out.println(m);
// System.out.println(m.get(53));
// System.out.println(m.get(30));
}
}